Preventing the Most Common Ladder-Related OSHA Citations
Top 10 Most Common OSHA Citations
Safety guidelines by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) are there to help keep you and your crew safe on the job. Although some of these rules may seem frustrating, they are necessary to follow- not only for the sake of preventing injuries, but also to avoid OSHA citations. According to OSHA.gov, the top ten most common citations are:
- Fall Protection
- Hazard Communication
- Scaffolding
- Respiratory Protection
- Lockout/Tagout
- Powered Industrial Trucks
- Ladders
- Electrical, Wiring Methods
- Machine Guarding
- Electrical, General Requirements
OSHA Ladder Safety
Two of the ten are directly related to ladders, so let's focus on how to prevent these citations by focusing on ways to better follow OSHA guidelines. Here are some of the regulations from OSHA for “portable ladders”:
- Become familiar with the labels/markings on the ladder.
- Look for overhead power lines before handling a ladder. Avoid using a metal ladder near power lines or other exposed energized electrical equipment.
- Always inspect the ladder prior to using it. If the ladder is damaged, remove it from service and tag until repaired or discarded.
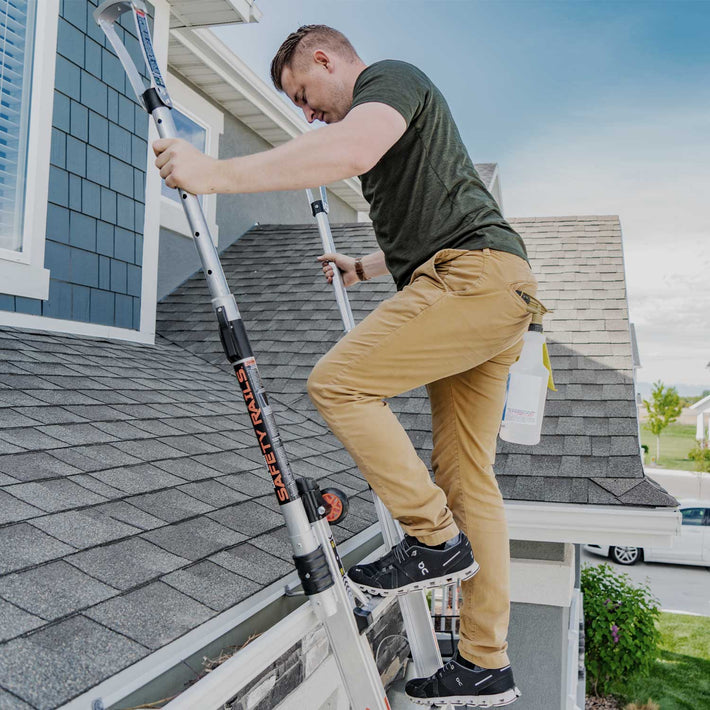
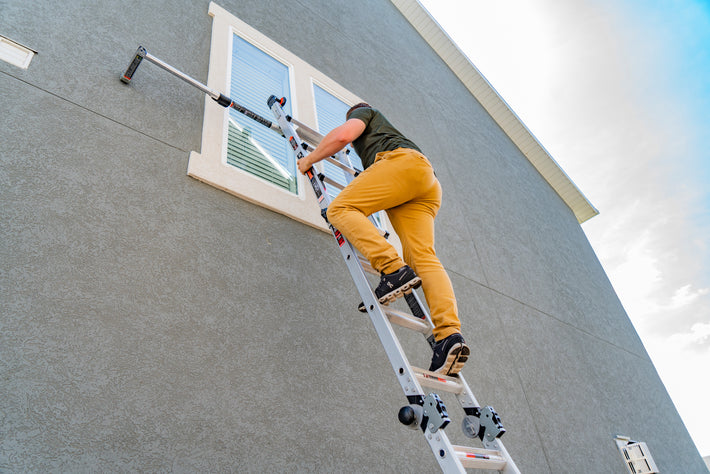
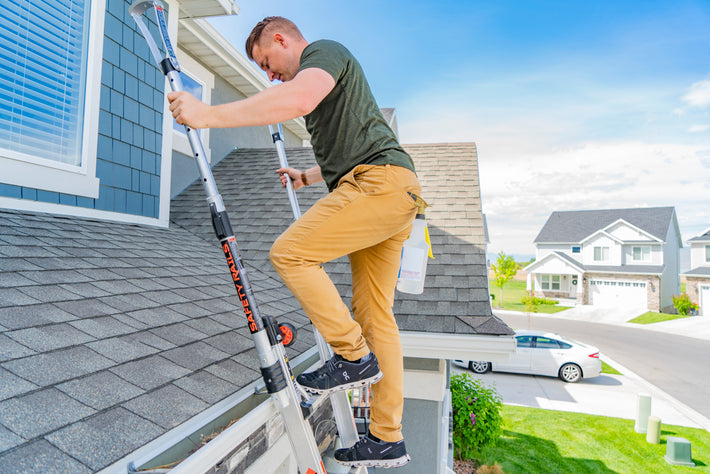
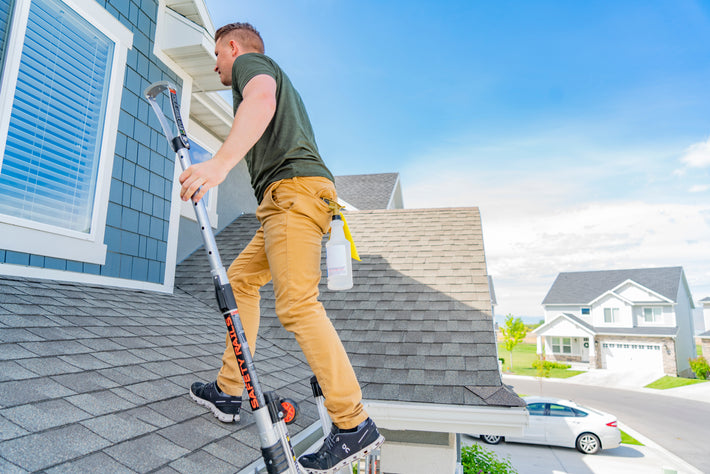
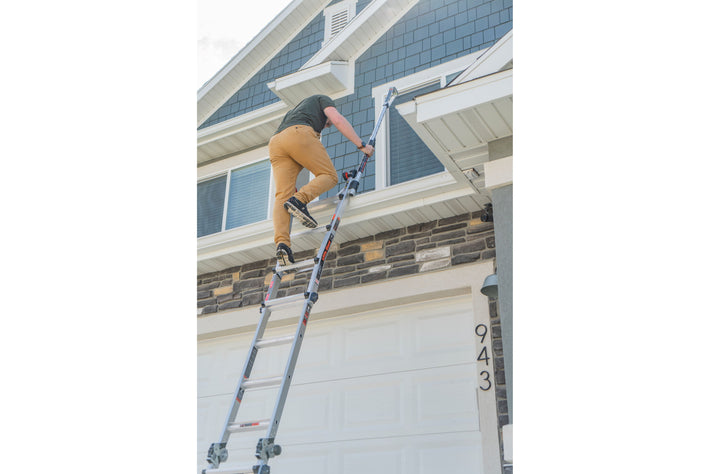
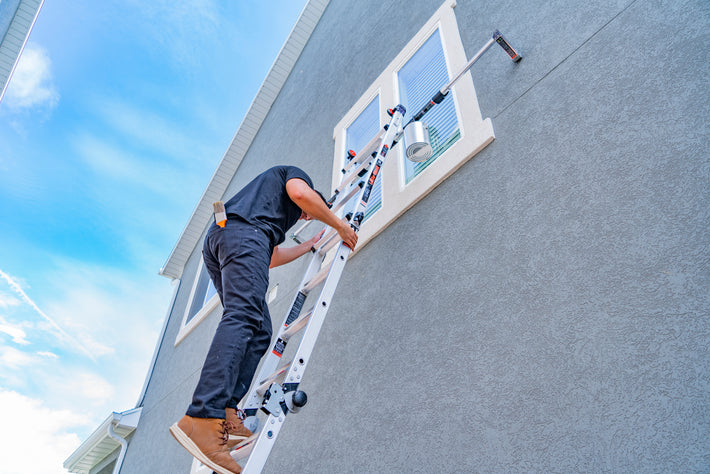
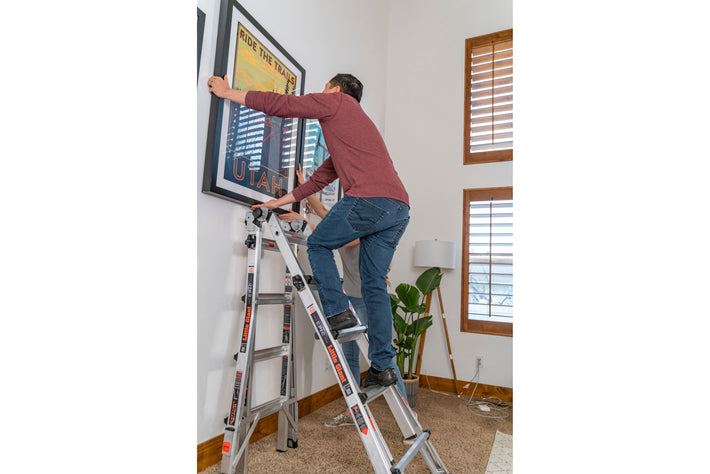
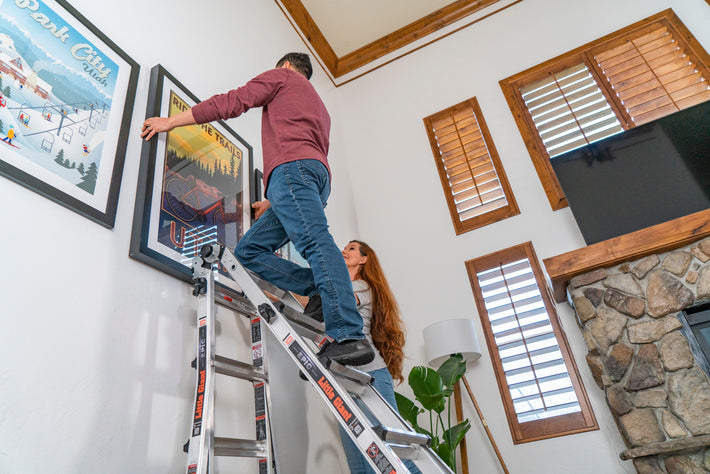
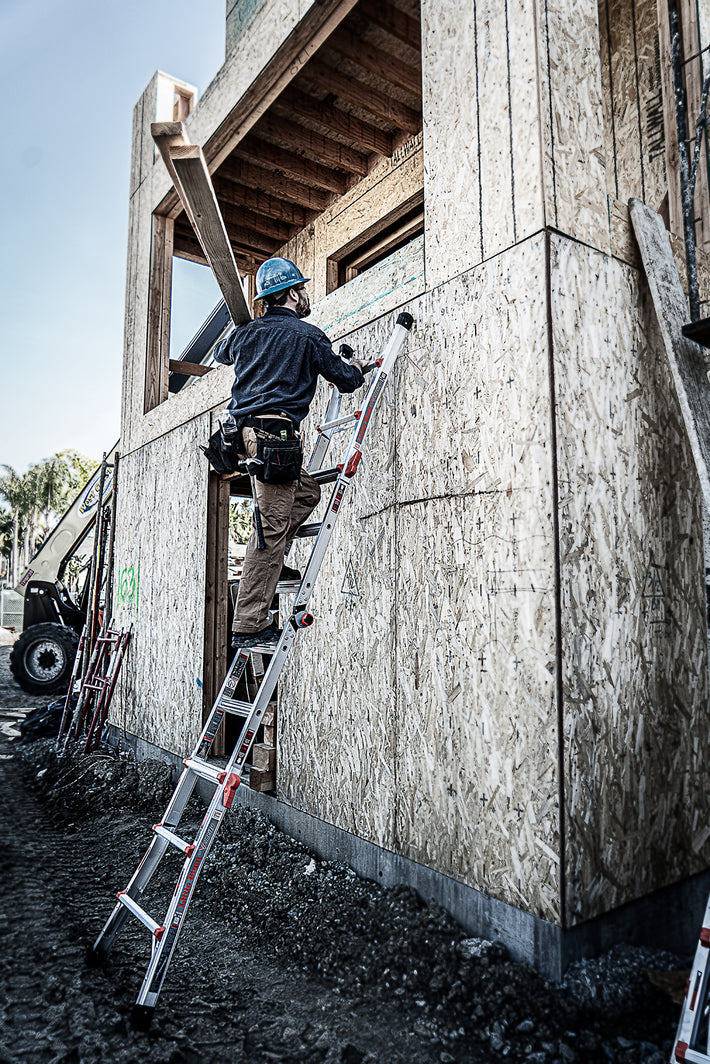
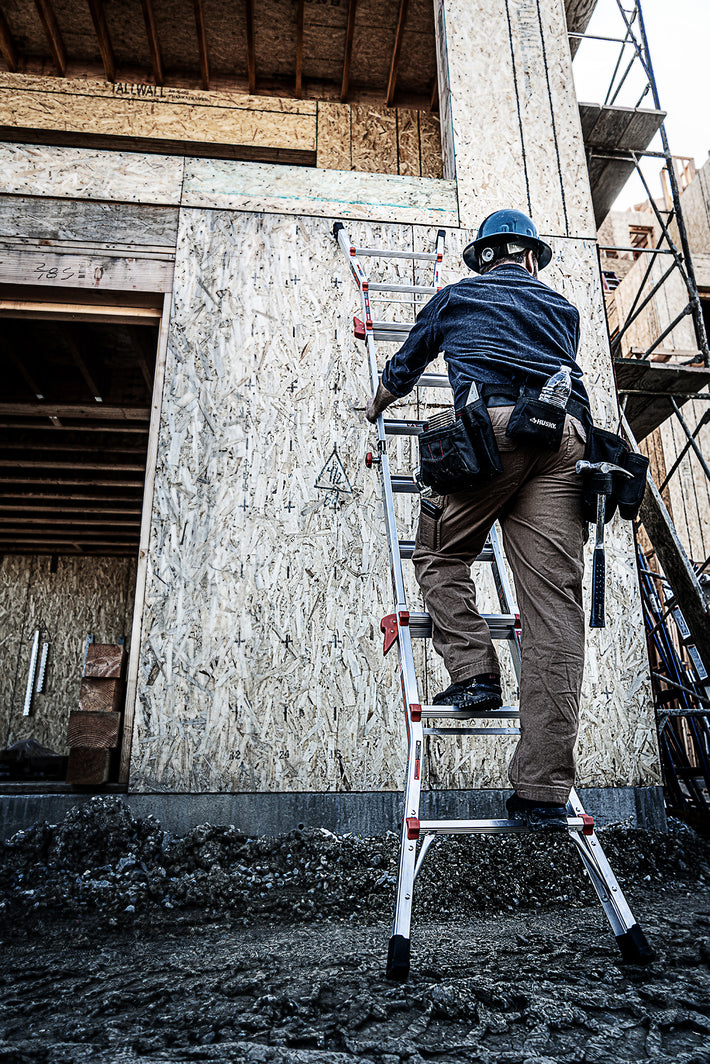
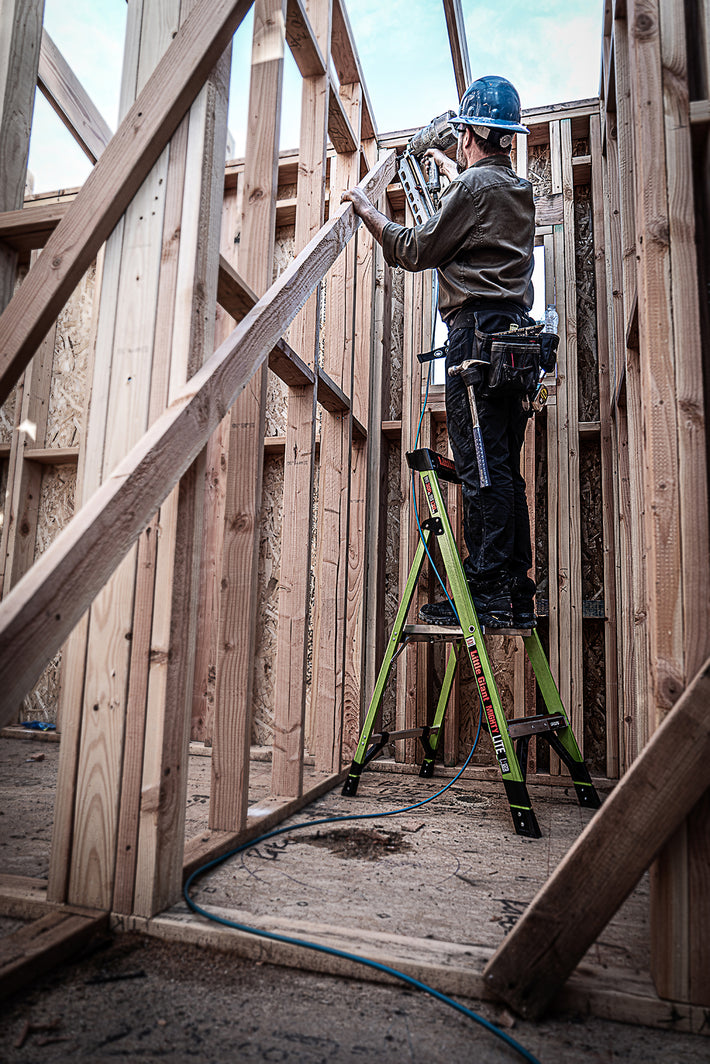
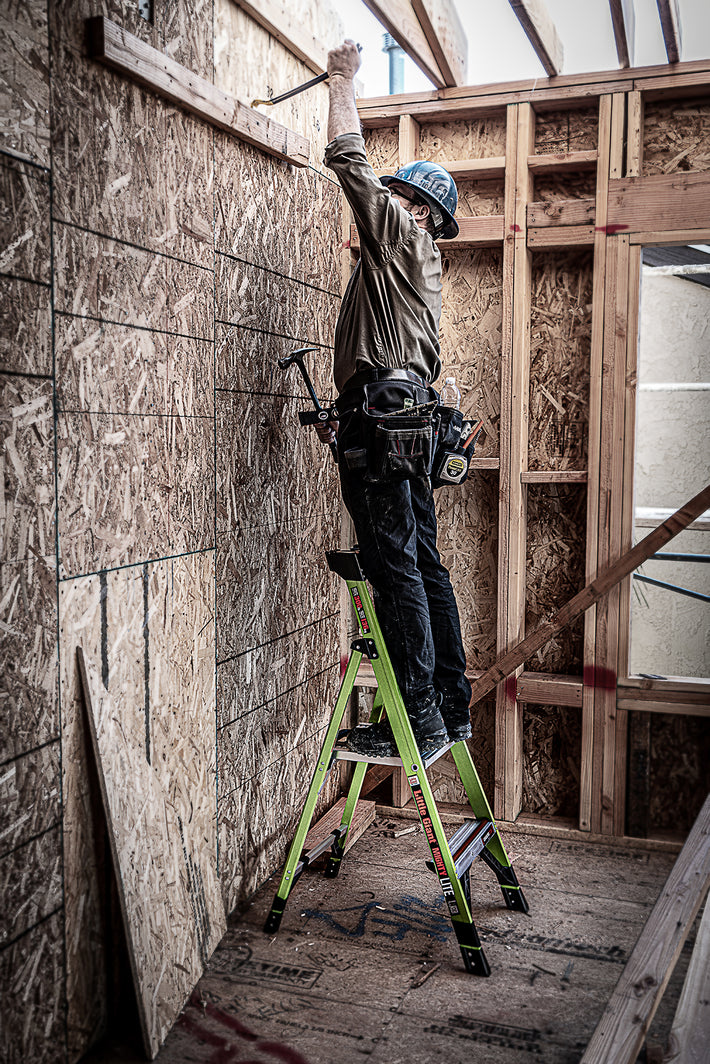
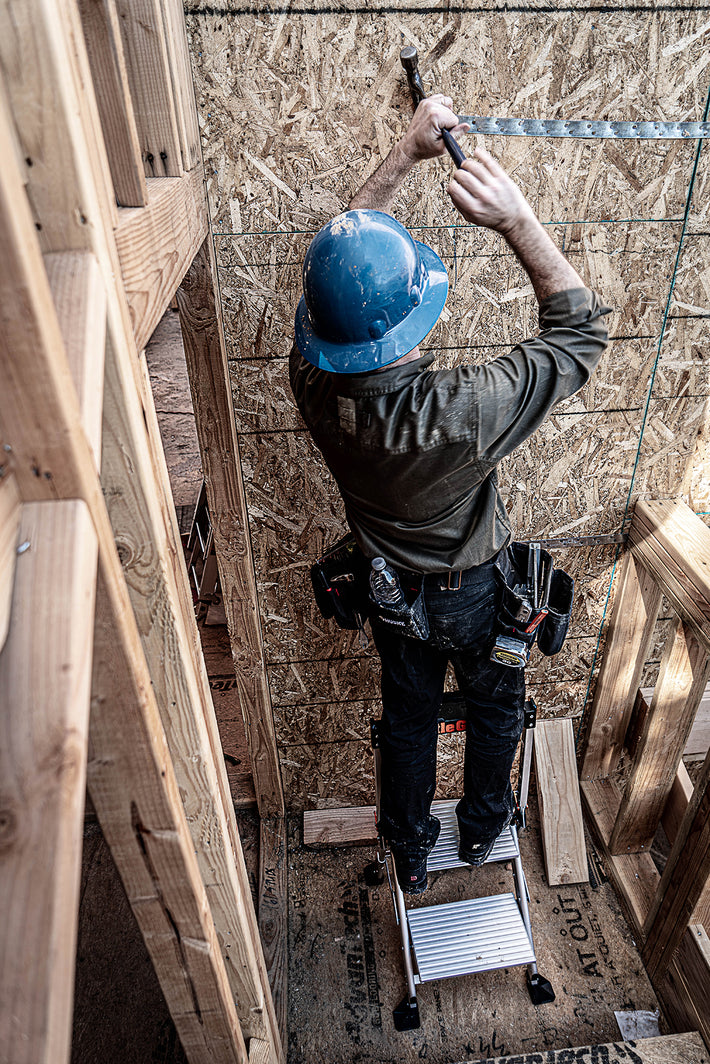
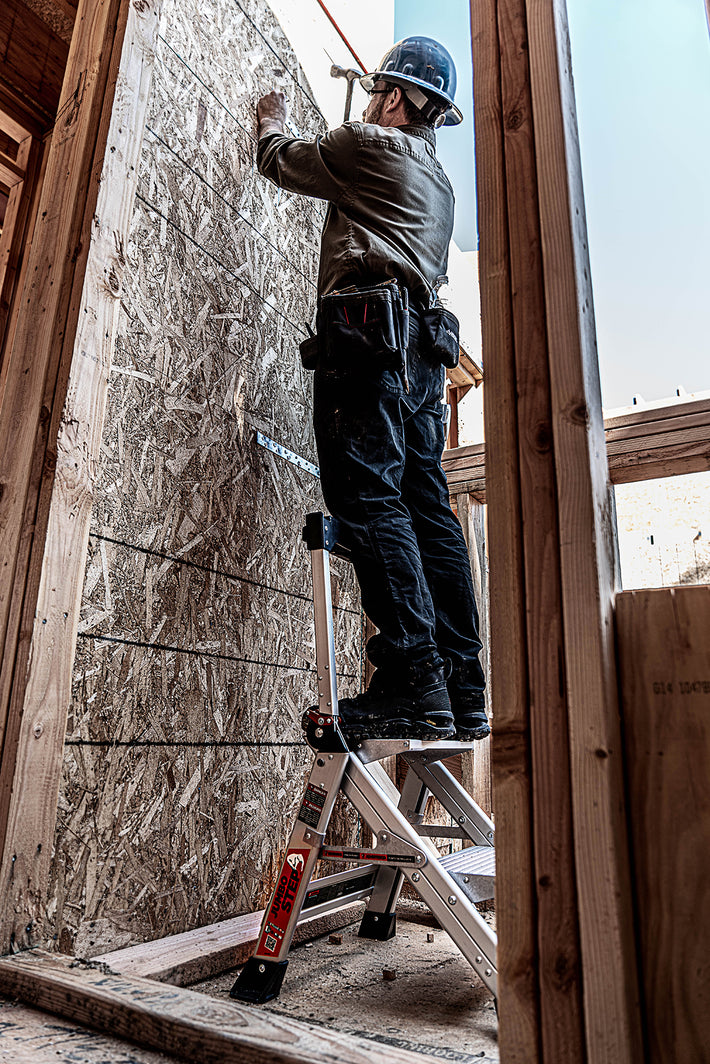
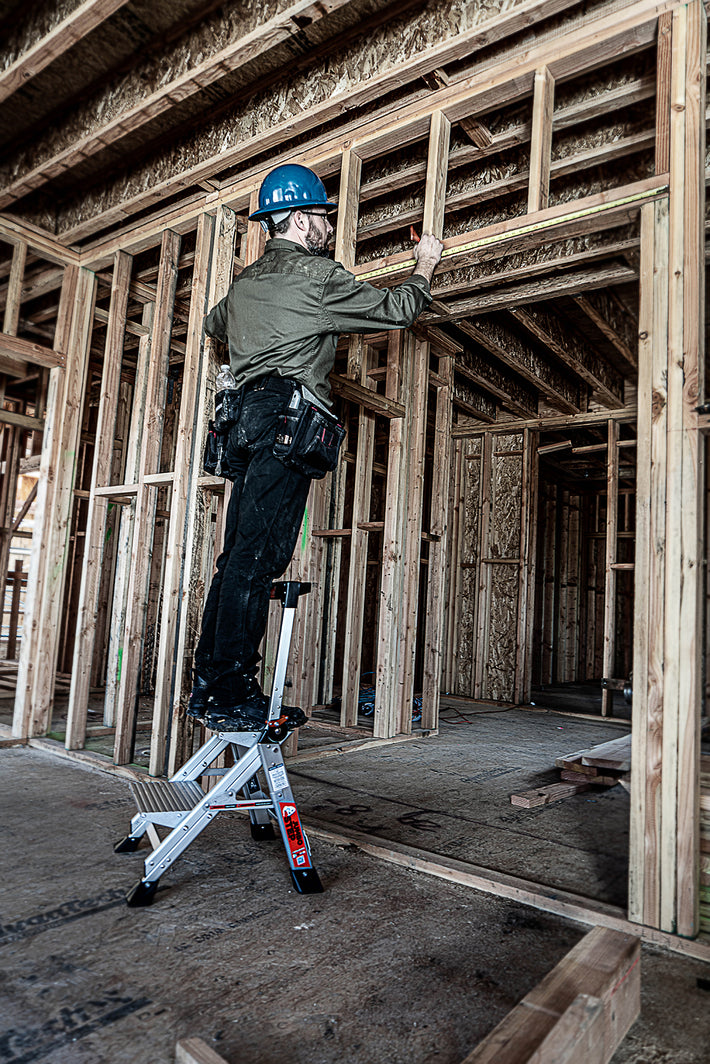
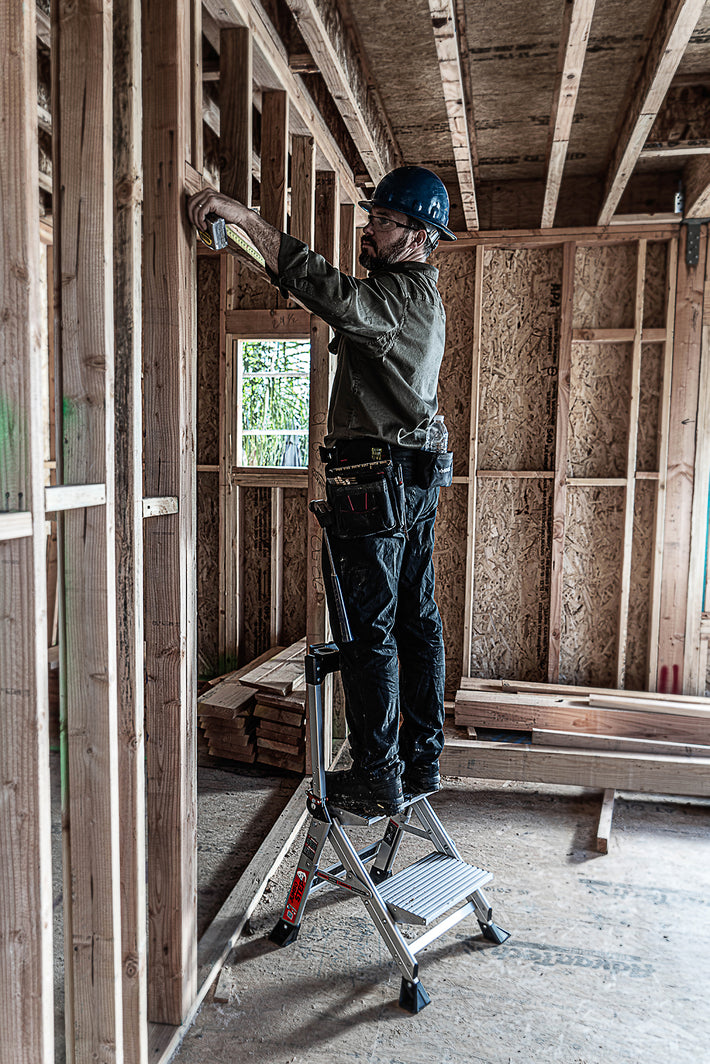
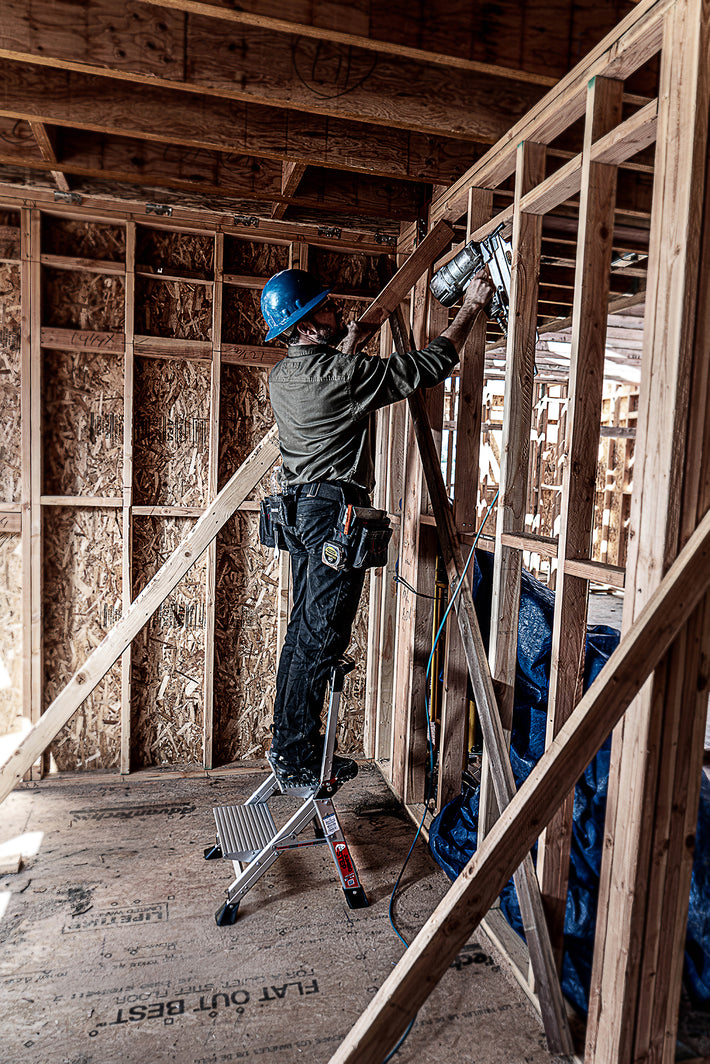
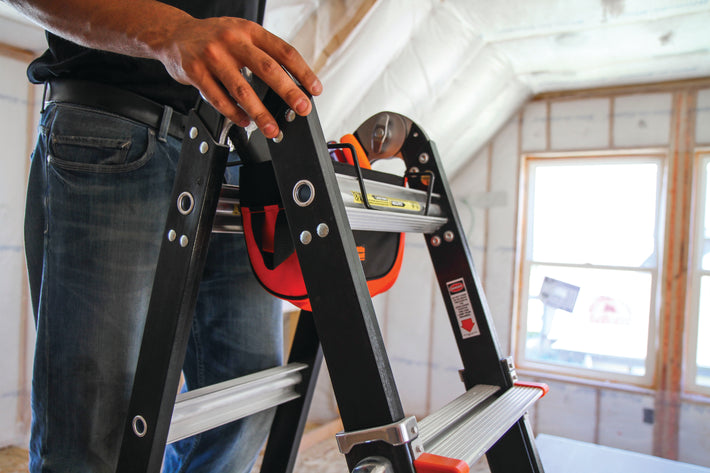
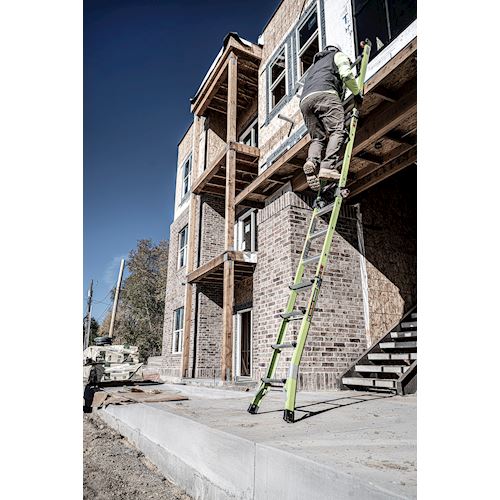
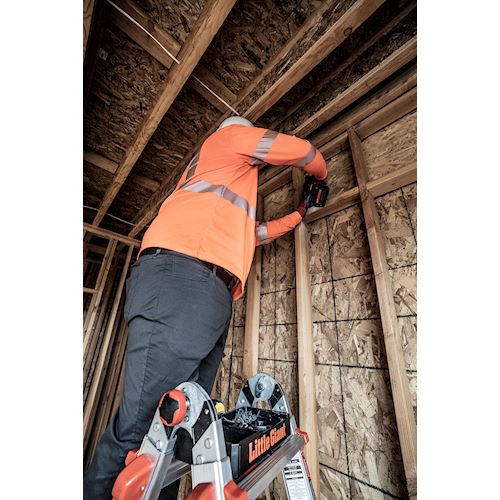
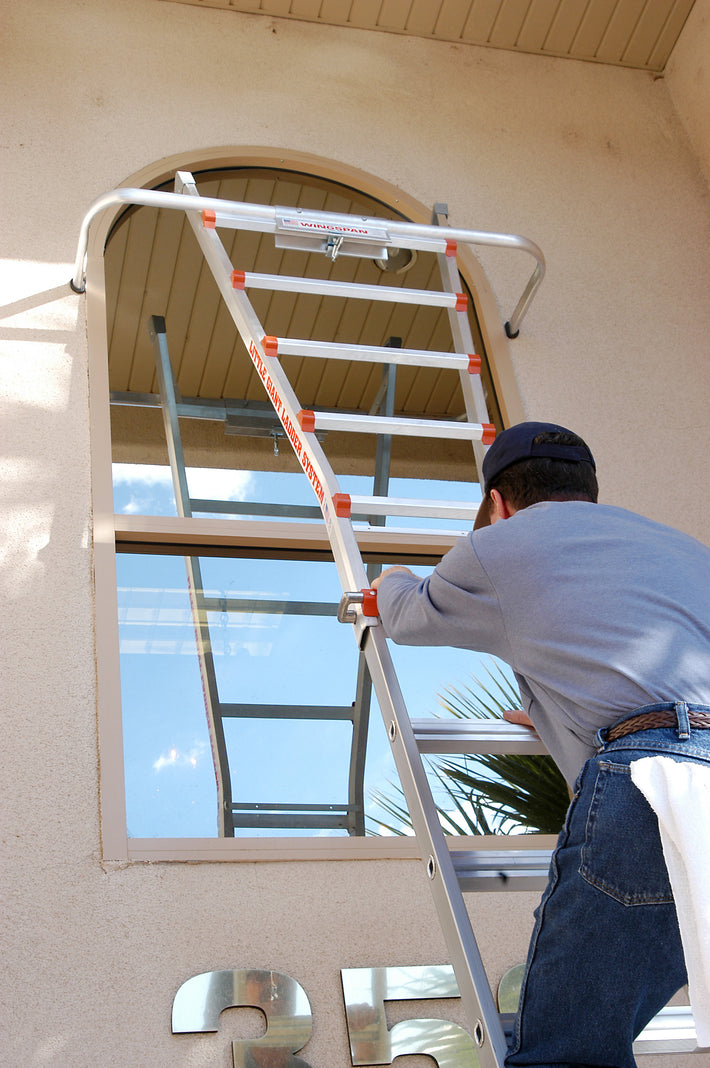
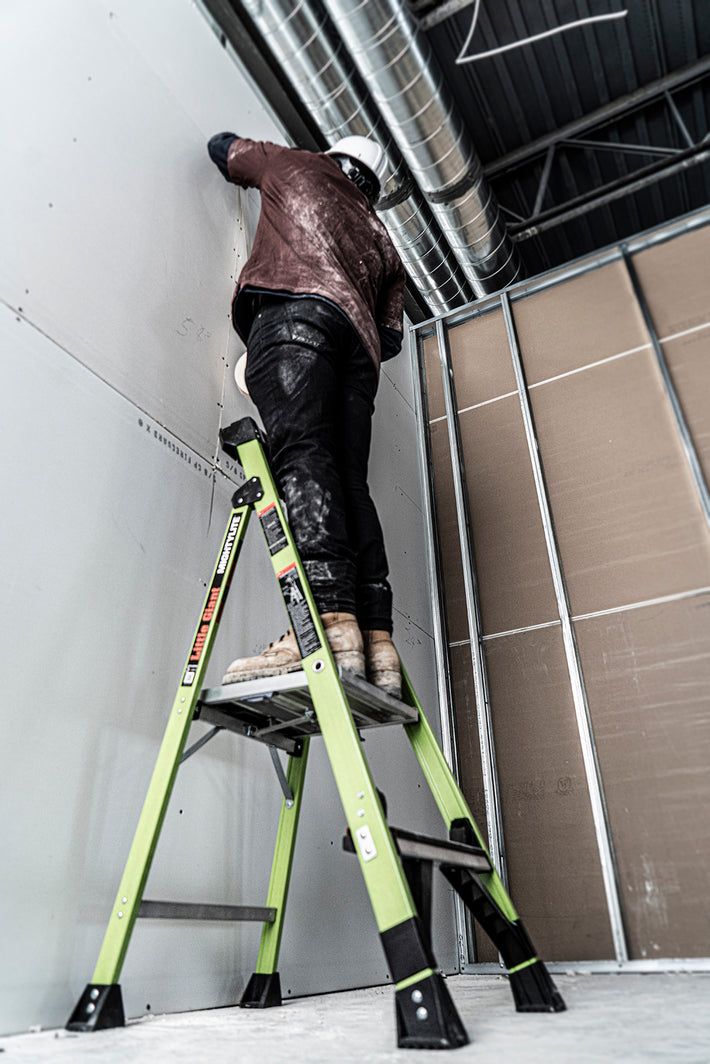
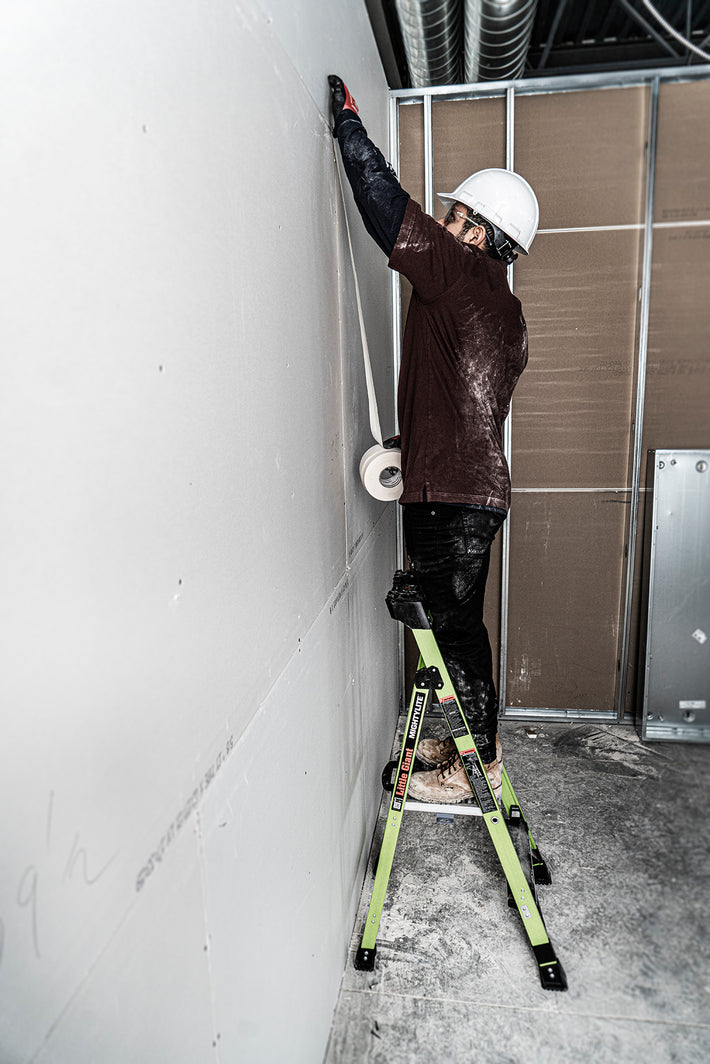
- Maintain a 3-point (two hands and a foot, or two feet and a hand) contact on the ladder when climbing. Keep your body near the middle of the step and always face the ladder while climbing (see diagram).
- Only use ladders and appropriate accessories (ladder levelers, jacks or hooks) for their designed purposes.
- Keep the ladder free of any slippery material on the rungs, steps or feet.
- Do not use a self-supporting ladder (e.g., step ladder) as a single ladder or in a partially closed position.
- Do not use the top step/rung of a ladder as a step/rung unless it was designed for that purpose.
- Use a ladder on a stable and level surface, unless it has been secured (top or bottom) to prevent displacement.
- Do not place a ladder on boxes, barrels or other unstable base to gain additional height.
- Do not move or shift a ladder while a person or equipment is on the ladder.
- An extension or straight ladder must extend at least 3 feet above the point of support. Do not stand on the three top rungs of a straight, single or extension ladder.
- The proper angle for setting up a ladder is to place its base a quarter of the working length of the ladder from the wall or another vertical surface.
- A ladder placed in any location where it can be displaced by other work activities must be secured to prevent displacement or a barricade must be erected to keep traffic away from the ladder.
- Be sure that all locks on an extension ladder are properly engaged.
- Do not exceed the maximum load rating of a ladder. Be aware of the ladder’s load rating and of the weight it is supporting, including the weight of any tools or equipment.
Workers sometimes forget this list of guidelines, which is what leads to accidents and injuries. Take some time on the job today to focus on how you are using your ladder. Follow the OSHA guidelines to prevent an onsite accident.
To learn more about ladder safety and ways to keep yourself and your crew safe on the job, check out Little Giant Ladder Systems' Safety Page. We have created climbing solutions that can keep you and your crew working safely and effectively.